- Understanding how solar panels work is essential, even if you’re hiring a professional installer. It enables you to communicate effectively with the installer, meeting your needs. Additionally, knowing the basics empowers you to validate their recommendations for your specific situation. After installation, this knowledge helps you monitor your panels to ensure they operate efficiently.
- Although not invented by one individual, solar energy has seen significant advancements over the centuries. Key contributors include Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel (1839), William Grylls Adams, Richard Evans Day (1876), and the Bell Laboratories team (1954). Their work on the photovoltaic effect and practical solar cells paved the way for modern solar technology, shaping its widespread global adoption.
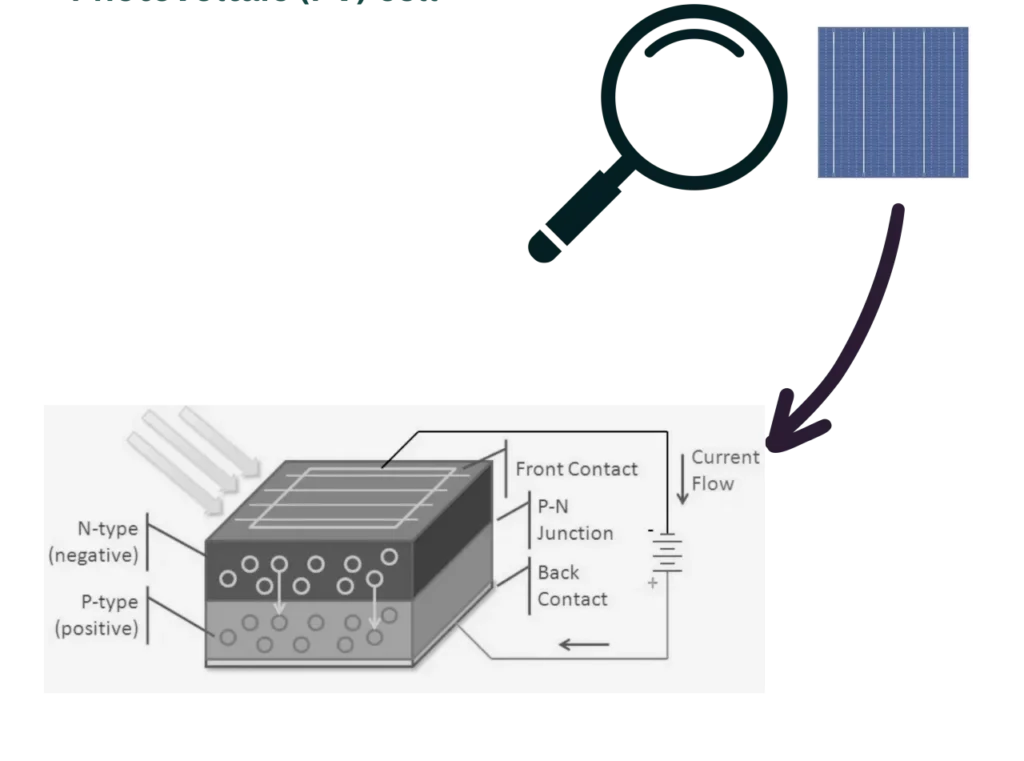
- A solar or photovoltaic (PV) cell is a semiconductor device that converts sunlight directly into electricity through the PV effect. Comprised of layers of semiconductor materials, such as silicon, the cell generates an electric current when photons from sunlight knock electrons loose, allowing them to flow through the material.
Photovoltaic (PV) Cell
- The most common types of solar cells are monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film. Monocrystalline cells offer high efficiency and longevity, while polycrystalline cells are cost-effective. Thin-film cells are lightweight and flexible, suitable for diverse applications.
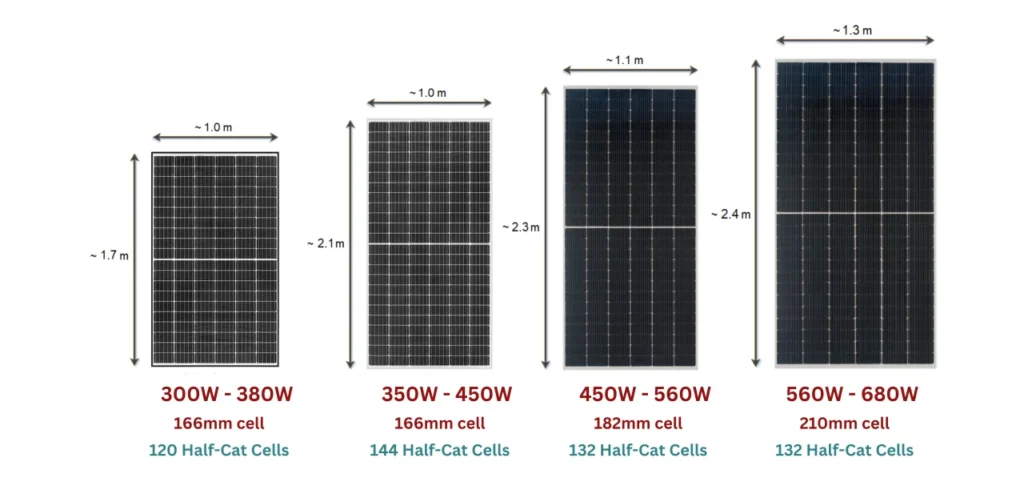
Solar PV Cell Size And Peak Output.

Voltage – akin to pressure in a pipeline, measured in volts (V).
Analogous to water flow in pipes, measured in amperes or “amps” (A)
Power – the combination of pressure and flow, measured in watts (W), represents the energy required to move water (or electric charge) through pipes.
Power – the combination of pressure and flow, measured in watts (W), represents the energy required to move water (or electric charge) through pipes.
DC (Direct Current) flows continuously in one direction, ideal for batteries and electronic devices needing steady, unidirectional power, like portable electronics and automotive systems.
AC (Alternating Current) reverses direction periodically, enabling efficient long-distance transmission and powering electric motors and household appliances. Power plants generate it and undergo voltage transformation and regulation for various applications.
In a parallel connection, components are linked across the same voltage source, ensuring they all have equal voltage. Current flowing into the parallel circuit divides among branches based on their resistance. If one component fails, others remain unaffected. Common examples of parallel connections include household electrical outlets and building wiring.
In a series connection, components are linked end to end, creating a single pathway for the current. Each component experiences the same current flow, and their resistances add up to the circuit’s total resistance. If one component fails, it disrupts the current flow throughout the circuit, potentially impacting all components. Common examples of series connections include strings of Christmas lights and specific types of battery packs.
- Half-cut solar cells, created by halving standard-sized cells, offer advantages such as reduced resistive losses, enhanced performance in shading conditions, improved durability, and higher efficiency. However, they come with potential disadvantages, including increased manufacturing complexity and potential cell mismatch.
Full and half-cut PV cells
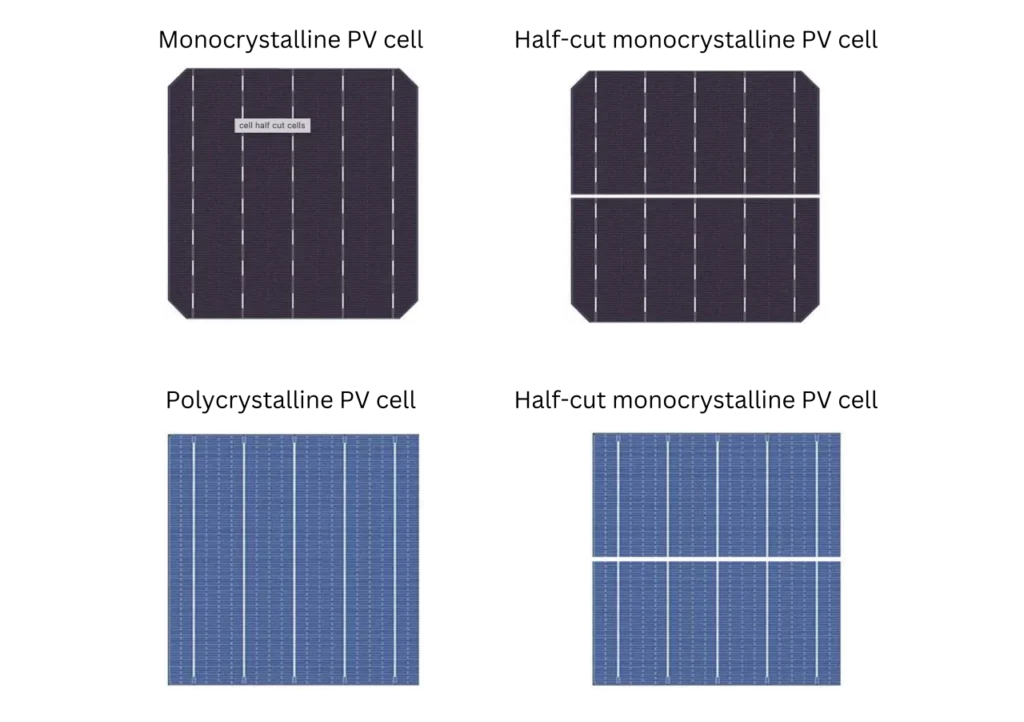
- Half-cut cells: Power range Varies, but it is generally higher than full-size cells due to reduced resistive losses and improved shading tolerance. Actual dimensions: Half of the standard dimensions, e.g., approximately 78 mm x 78 mm for half-cut 156 mm cells.
- A solar or PV (photovoltaic) panel typically consists of interconnected solar cells framed in aluminum. The aluminum frame provides structural support and protection for the solar cells while allowing for easy mounting and installation onto rooftops or other structures.

- While a solar cell generates a small amount of electrical power, a solar panel combines and interconnects numerous cells to produce a higher voltage and power output. In essence, the nominal power of a solar panel is the sum of the power output of all the cells of the panel.
Solar Panel Size & Power
- Alternating current (AC) periodically changes direction, facilitating efficient transmission and compatibility with transformers. Direct current (DC) maintains a constant flow in one direction, ideal for batteries, electronics, and specific applications. Solar panels generate DC electricity, but homes typically use AC, requiring inverters to convert the power for household use.
- Inverters also adjust the voltage levels to match the requirements of household appliances and the electricity grid. For example, a panel can generate 450V, but our home grid is 220V.
- Standard inverters, or grid-tied inverters, convert solar panel-generated DC electricity into AC electricity for immediate use or export to the grid. They lack battery integration and offer no backup power during outages. In contrast, hybrid inverters combine solar and battery functions, enabling energy storage and backup power capabilities and providing greater energy independence.
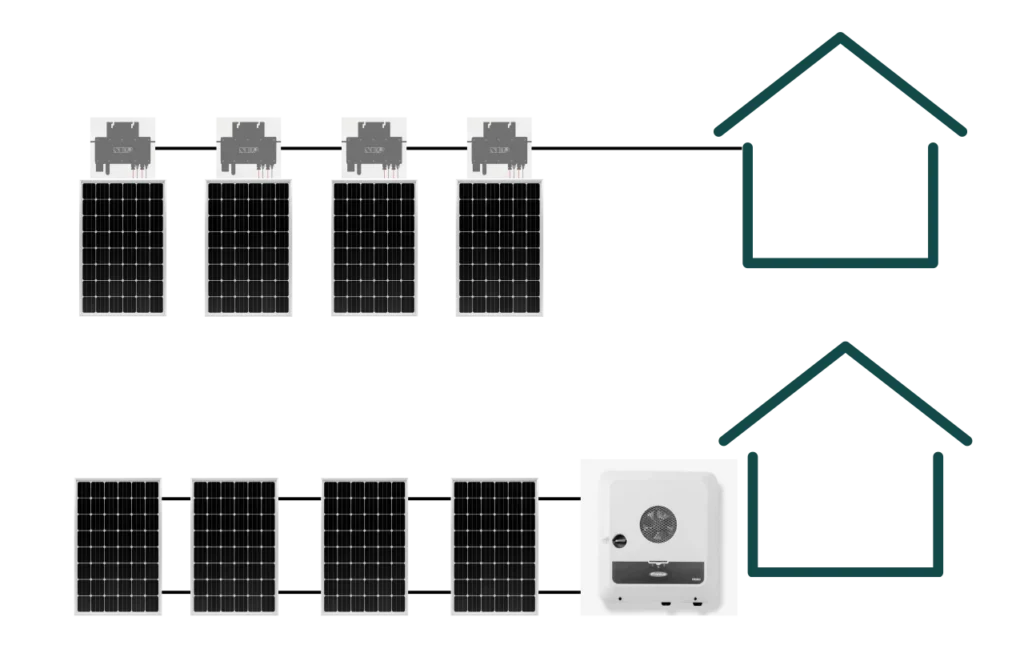
- Micro-inverters are installed on individual solar panels, independently converting DC electricity to AC, optimizing performance, and offering panel-level monitoring. Central inverters, installed centrally, convert combined DC electricity from multiple panels into AC. They are cost-effective and simpler to install but lack panel-level optimization. The choice depends on system size, shading, monitoring preferences, and safety requirements.
Microinverters connect panels in series and central inverters in parallel.
- Inverters generally have efficiency ratings ranging from 90% to 99%, indicating the percentage of DC electricity converted into usable AC electricity. Optimal systems can achieve efficiencies nearing 99%, maximizing energy conversion and system performance, while less efficient models may fall closer to 90%, resulting in higher energy losses.
- Inverters are the most loaded equipment in solar stations. The warranty period is crucial as it guarantees the reliability and longevity of the inverter, ensuring uninterrupted operation and protecting the investment in the solar PV system. Typically, warranties for inverters range from 5 to 25 years, depending on brand quality.
- Optimizing solar farm efficiency demands precise alignment of every system element with both internal and external conditions. From mitigating shading to orienting panels to the sun’s path and ensuring proper placement of ancillary components, meticulous alignment maximizes sunlight exposure and energy production.
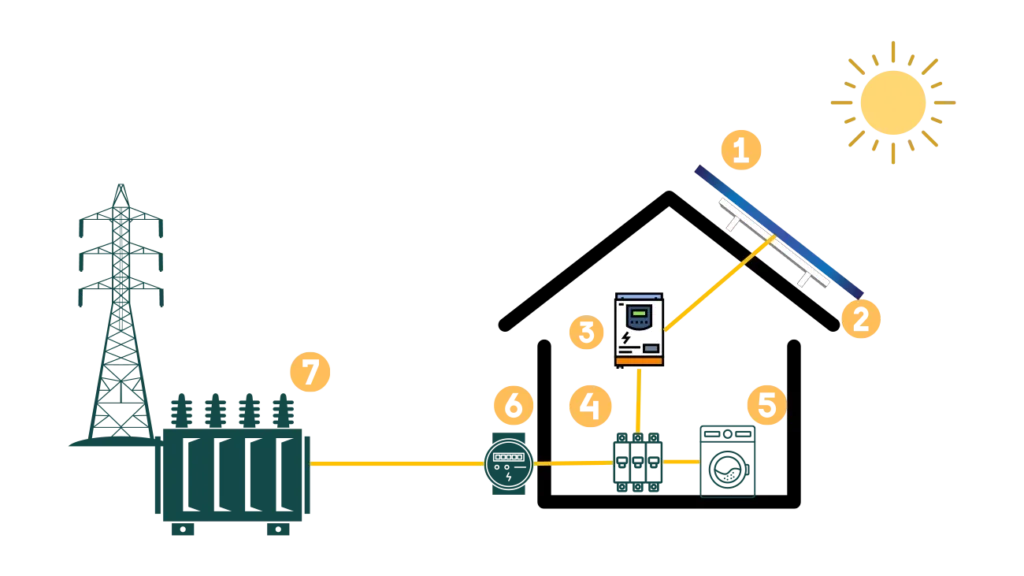
(2) They are installed on special racking, which secures the panels to the roof.
(3) The inverter then transforms DC electricity into home AC electricity.
(4) The inverter sends AC electricity to your main panel.
(5) The home appliances get electricity from your main pane.
(6) The solar meter records the watts received from and sold to the grid.
